Listening Module in IELTS
IELTS Listening Module is
appeared in the beginning of the test. The Listening test is the same for both IELTS Academic test and
IELTS General Training test. It consists four different parts. Each
parts has ten questions where you will get 30 seconds pauses in the middle of
the questions except in part 4. You will have 1 to 40 questions which you hear
only once the audio clips. You will have 30 minutes average time to hear the
audio where you will be provided British, American and Australian accents.
Later, you will have 10 minutes extra time to transfer your answers to the
answer sheet.
IELTS Listening Answer sheet
Let's learn about the
different parts of listening and how they appear in the exam.
Part-1
This section is the
easiest section. Speaker talks quite slowly making pauses. The key information
is usually repeated.
Examples: two people talking about their journey, asking
about the destination, one is giving advices to another about a new project,
two men are discussing about the result of football match, tourist registering
at the hotel etc. You have to focus on the given facts (information).
Part-2
A monologue about
everyday situation where the speaker talks quite slowly, but makes less pauses
than in previous part
Example: information for
potential buyer about new built flats, radio interview about lake resort,
advertisement about positive effect of a new toothbrush etc. You have to focus
on the given facts (information).
Part-3
It is a conversation
about 2, 3 or 4 speakers about educational (academic) or training situations.
This part is
comparatively difficult than the two previous parts. Speakers talk at a faster
pace and sometimes they use advance vocabularies. Examples: a university tutor and students
discussing an assignment, people talk about the professors'
academic speech etc.
Focus on the given facts,
key ideas and the speaker's opinions and attitudes.
Part-4
It is an academic
subject. It is the most difficult part. There is no break in the middle, the
speaker talks quite quickly and uses a wide range of vocabularies.
Examples: lecture
about endangered species about global warming and its effects, talks about how
to bring up children, lecture about forest reserve, a university lecture etc.
Focus on the given facts,
key ideas and the speaker's opinions and attitudes.
A wide range of English
accents and dialects are used in the recordings which reflects the
international usage of IELTS.
|
Context (every part of
listening) |
Number of speakers |
|
1.
Social needs |
conversation
between two speakers |
|
2.
social needs |
speech
by one person/speaker |
|
3.
Educational or training |
conversation
between up to four speakers |
|
4.
Academic subject |
speech
by one person/ speaker |
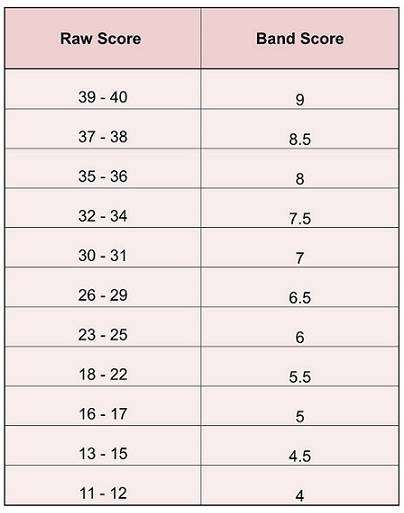
You can calculate your Band score by counting up your marks out of 40 and comparing them with the scores below:
Top 5 IELTS Listening Tips
1.
Familiarize yourself with a range of accents.
2.
Don’t lose your
concentration.
To improve your concentration you need to practice active
listening.
3.
Follow the instructions
carefully.
This especially applies
when it comes to the word limit. If the question states ‘No more than three
words’ then you can’t write any more than this. If your answer is four words it
will be incorrect.
4.
Familiarize yourself
with the different question types.
Doing so will mean
you’ll know exactly what to expect on test day and how to react to the question
types you’re given.
5.
Practice listening only
once.
1.
Matching Questions
2.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
3.
Note completion
4.
Form completion
5.
Table completion
6.
Sentence completion
7.
Summary completion
8.
Short answer question
9. Map and plan labelling
Diagram and flow chart completion
1. Matching Questions
Candidates are
given a list of items from the audio and are requested to match it with a set
of options on the question paper. The set of options might be criteria of some
kind. The questions will be sorted following the listening text order in the
record. The information part will be a list of answers to match, they are in a
random position, not following any specific order.
Example:
In multiple choice questions, you are required to
choose the correct answer from a list of options. There are two main types of
question:
i.
Single
questions with a choice of 3 answers (A,
B or C). Occasionally, there may be 4 options.
ii.
List questions. These have a longer list of possible
answers and you must select more than one as specified in the question.
The Strategy
1) Read the
question
2) Look for a
title
3) Underline the
key word in the question
4) Predict the
answer
5) Think of
synonyms
6) Identify the
difference
7) Watch out for
distractors
8) Writing the
answer
9) Guess if necessary
3. Note Completion
Note completion
questions come up regularly in the IELTS Listening exam so there’s a high
chance of you getting one in your test. They can take many different forms but
will always be a gap fill activity of some sort where you have to fill in
missing words. You could, for example, be asked to fill in missing words in a
set of notes from a lecture or a list of instructions for a journey. It’s also common to make notes, for
example, during meetings and telephone conversations or when browsing the
internet for information on a particular topic, such as travel information for
a holiday.
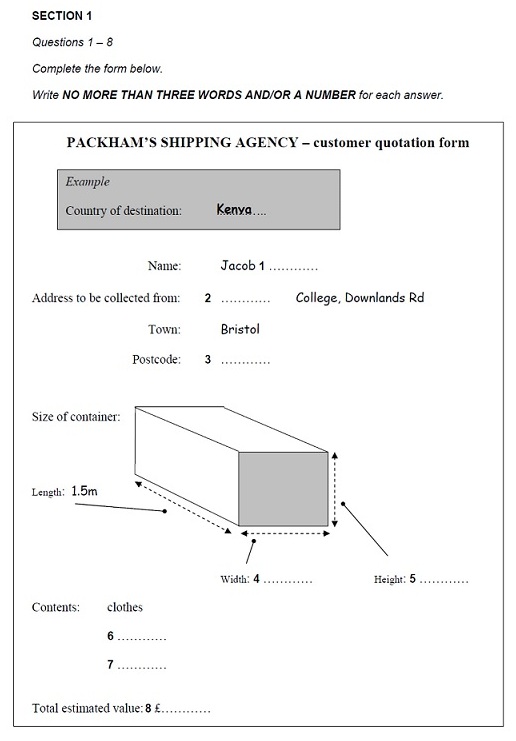
4. Form completion
Form completion questions are one of the easiest types of
IELTS Listening questions to answer as long as you know how to recognise and
write the vocabulary they typically contain. Form completion questions are
common in Section 1 of the test and the recording will often be
a telephone conversation between two people.
The two most common
types of form you’ll see are:
- An application form
- An order or quotation form
Application Form
The recording for this sample question is
a telephone conversation between the Youth Council administrator and a young
man who wants to apply for election to the Youth Council.
Quotation Form
5. Table completion
Table completion
questions come up regularly and can appear in any section of the test.
Table completion
questions are gap fill questions that require you to fill in missing words. The
table will be made up of columns and rows containing information.
Generally, tables
categorise information, that is, they group pieces of information that are
related in some way or share the same features. It follows an order.
6.
Sentence completion
Sentence completion questions are one of
the less common types of IELTS Listening questions but you need to know how to
answer them in case you do get one.
They are a type of gap fill question
where you must listen to the recording and fill in the missing words in the
sentences to complete them. It's very often the ending of the sentence that
you'll have to complete but you may also have to fill in words within
sentences.
Sentence completion questions can appear
in any section of the IELTS Listening test but as long as you have a good
strategy to follow, you’ll be able to answer them successfully. Occasionally,
you may be able to predict the actual word but it should certainly be possible
to determine the type of word needed to fill each gap, such as,
a noun, an
adjective, a verb, adverb, number
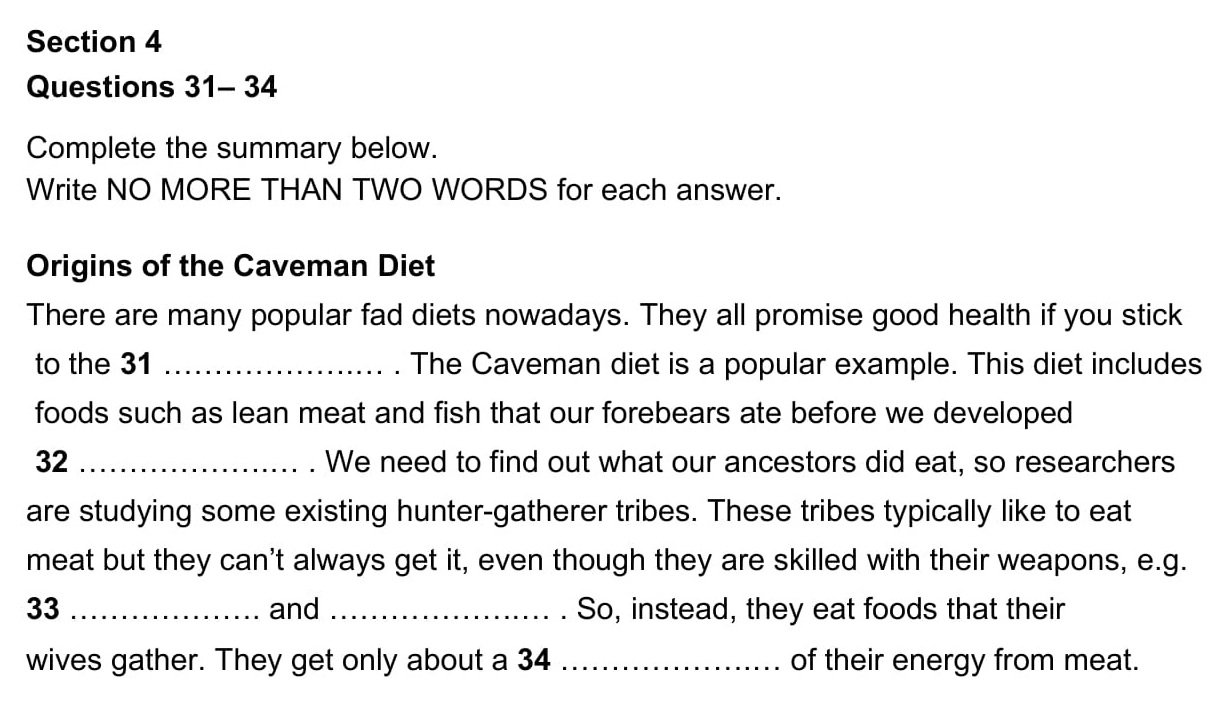
7. Summary completion
Summary –
a short, clear description that gives the main facts or ideas about
something
For summary completion questions,
you'll be given a summary of the recording. The recording will typically be a
monologue on an academic subject such as a lecture on the Amazon rainforest or
the Pyramids at Giza. There will be words missing from the summary which you
must fill in.
This type of question is most likely to
come up in Section 4, the most challenging part of the test. Occasionally,
you’ll be able to predict the actual word but mostly it’s one or more of these
things that you’ll be able to determine:
- The type of information required,
e.g. name of a person, place name, number, date.
- The type of word required, e.g.
noun, adjective, verb.
8.
Short answer question
These come up regularly in the exam and can
appear in any section of the test. They are particularly common in Section
2 which will be a monologue set in an everyday social
context, for example, a welcome talk for new college students.
You must listen to the recording and
write a short answer in each blank space provided. Synonyms and paraphrasing
will be used extensively in the recording. So, you will not only be listening
for the exact words that are used in the questions but also, different words
and phrases that have the same meaning.
In your preparation time, scan the
questions and underline key words that are likely to be replaced by synonyms or
paraphrased. Then, quickly think of words that might be used instead.
Occasionally, you’ll be able to predict
the actual word but mostly it’s one or more of these things that you’ll be able
to determine:
- The type of information required,
e.g. name, date, time, phone number, address, price.
- The type of word required, e.g.
noun, adjective, verb.
Sometimes, more than one answer will be
required, for example,
What are the TWO major
concerns new students have regarding accommodation?
sample 1
Sample 2
9.
Map and plan labelling
These come up regularly in the exam and are particularly common in Section 2. The subject for plan questions will typically be a tour of a specific building such as a hotel or museum, or the description of a place. In map questions, the speaker will often talk about proposed changes to a location.
Your task is to listen to the recording
and identify different areas, features or rooms. You will often be
given a list of words from which to choose the correct answers. If no list
is given, you will have to identify the answers from the recording. Many students find these one of the easiest question
types to answer because the graphic will contain lots of clues as to the
missing words, especially in the labels already present.
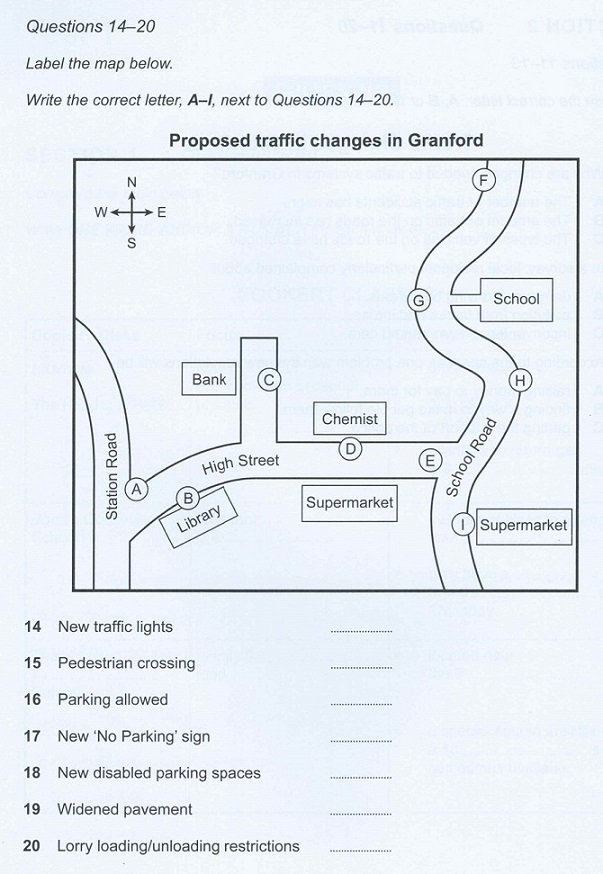
In the recording for this sample question, the chairman of the Highways Committee is explaining the new traffic regulations and parking arrangements proposed for Granford at a public meeting.
In the recording for
this sample question, the chairman of the Highways Committee is explaining the
new traffic regulations and parking arrangements proposed for Granford at
a public meeting.
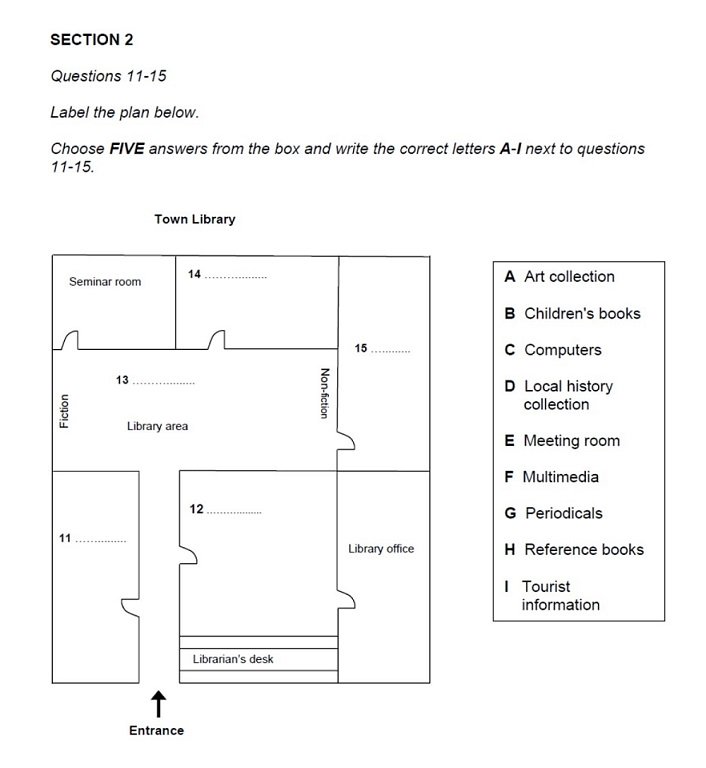
For this question, the
speaker is the librarian of a new town library. They are talking to a group of
people who are visiting the library.
Strategy & Tips
You will have a short time to prepare
before the speakers begin talking. Use this time to familiarize yourself with
the question and focus your mind on what you need to listen out for.
1) Read the instructions
Read the instructions very carefully
as the wording, and what you have to do, vary in this type of question. For
example, the instructions for the first sample question state:
Write the correct letter, A–I, next to
Questions 14–20
Very important: Write only
the letter (A–I) on the plan. Do not write the
word. If you do, your answer will be marked wrong.
So, if answer 11 was
’computers’, your answer would be 11 C, not 11
computers.
2) Read the labels & title
Learn as much as you can about the map or plan
from the existing labels, and the words in the answer list if there is one.
Some maps and plans will also have a title which is another big clue as to the
context of the question and what the recording will be about. For example, the
question in IELTS Listening Sample Test 1 above, has the title ‘Proposed
traffic changes in Granford’. Knowing this should bring a few ideas to mind as
to the sort of information that will be included in the audio text. The more familiar you are with the vocabulary and the
layout of the graphic, the easier it will be to understand and follow what the
speaker says.
If there is no words
list, try and predict what type of word the answers will be from the context of
the plan or map, for example, is it a room, a building, a street, a feature
such as a pond or a facility such as a public toilet.
Generally, the speaker
will begin their talk by introducing themselves and the subject or purpose of
the talk so this will also help you to understand the context.
3) Visualization
One of the skills needed to answer map
and plan questions successfully is to be able to visualise what the place being
described looks like.
We use maps and plans in everyday life so
your brain will already be used to doing this, although you normally do it
subconsciously without even thinking about it.
4) Answer order
The answers will come in the same order
in the recording as they are listed in the question so, for our sample
question, you'll hear answer 11 first, then answer 12 and
so on. This makes it easier to pick out the answers than if they were in a
random order.
5) Vocabulary
To do well in map and plan questions, you
need to understand the language of location and direction.
- Location – where something is in relation to
another object or place.
- Direction – the position towards which someone moves
or faces
Common vocabulary of location:
- near
- next to
- in front of
- beside
- between
- across from
Common vocabulary of direction:
- turn right
- turn left
- go straight
on
- go past
- head
south
- northwest
6) Synonyms and paraphrasing
7) Watch out for distractors
8) Guess if necessary
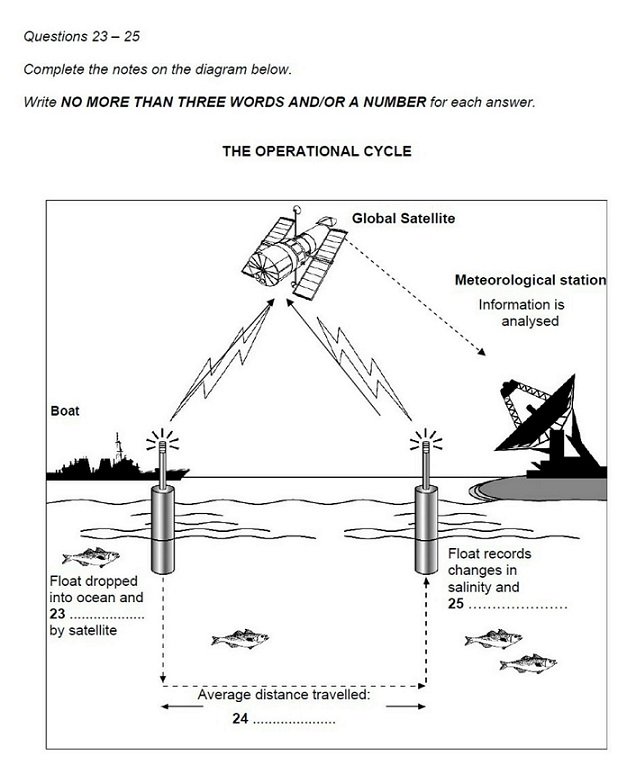
10. Diagram and flaw-chart completion
Diagram labelling
In diagram labelling questions, you will
be given a diagram of a process, an object, a structure or a machine and you
must either fill in the missing labels or complete notes within the
diagram.
You could get almost any topic. Examples
of diagrams from past papers have included a beehive, a soda can, a fire
extinguisher, a Ferris wheel, a zip fastener, a solar heating system, an
undersea turbine and soil layers.
As long as you have a good strategy to
follow, you’ll be able to answers questions on any subject. In fact, students
generally find this one of the easiest question types to answer because the
graphic and the existing labels give lots of clues as to what the missing words
might be.
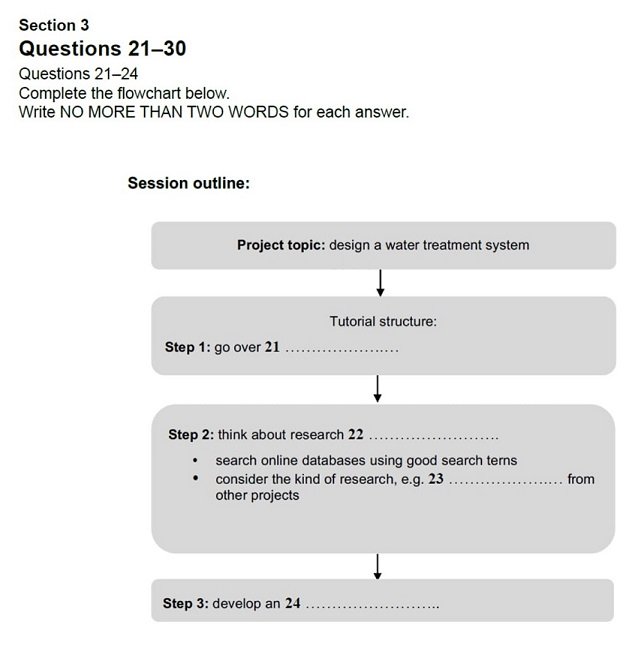
Flowchart Completion questions, on the
other hand, show the steps of a process. The process will have a start and
an end with several steps in between.
It could be about almost anything that
can be broken down into stages, for example, the outline of a lecture or essay,
an application process, the stages of a training course or a short
manufacturing process.
The graphic in the sample question below
shows the 3 stages of a project to design a water treatment system. Like most
flowchart completion questions, it occurs in Part 3 where the recording will be
a conversation between up to four people set in an educational or training
context.
By Bal Ram Shah











No comments:
Post a Comment