IELTS
Reading tests are different for Academic and General IELTS. As you may know,
you should take IELTS Academic module if you're going to study abroad. And if
you're intending to work abroad, then you should take IELTS General module.
IELTS Academic reading is more challenging than IELTS General reading.
Both General
and Academic IELTS Reading tests have 3 sections with 40
questions in total. IELTS Reading test lasts 1 hour.
|
Time |
60
minutes |
|
Questions |
1- 40 |
|
Sections |
3 passages |
IELTS
Academic Reading
This module
takes 60 minutes and has 3 sections. Each section has from 10 to 17 questions,
making 40 questions in total. Questions become more difficult throughout the
test.
IELTS
Academic Reading information:
•
Texts
are taken from books, journals, newspapers, magazines and web-sites that cover
academic topics for non-specialist audience.
•
All
three sections contain 2,150-2,750 words in total.
•
One
of the sections may contain graphs, charts, illustrations or other non-verbal
material.
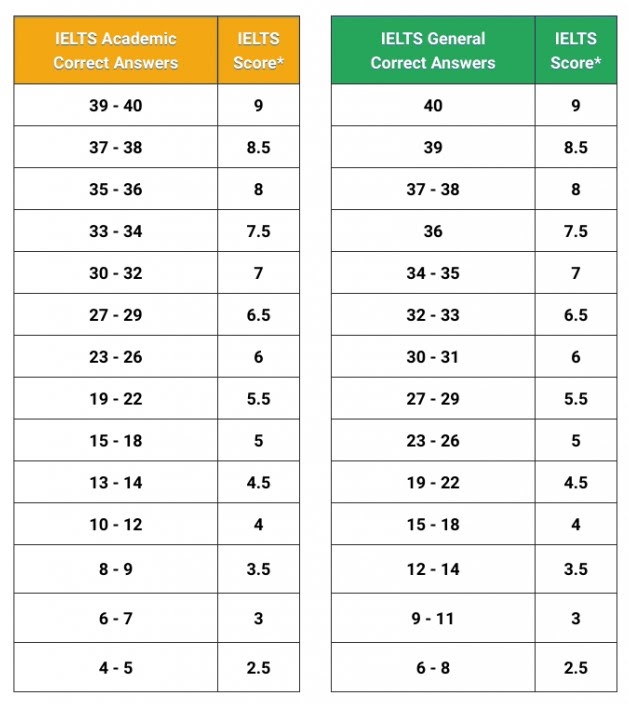
IELTS
Academic and GT/UKVI Reading marking scheme
Each of the
40 questions is worth 1 point. Depending on how many points you gain, you can
receive a score from 0 to 9 points for the Reading Section. To determine
your IELTS Academic and GT/UKVI Reading score, the following conversion
table applies:
1. Skimming: searching for a general overview or to look for the main idea
of the paragraph
It is
reading fast in order to find the overall meaning of the text. This can be used
when you need to find the main idea or information. You can save your time by
doing it.
2. Scanning: to find specific information, you use this method to search
for the key words
It is also
fast reading to find the particular person, place, date, time etc. Scanning is
required you to keep patience and away from tiring.
What are the key words in IELTS?
Keywords
are the words that carry specific information. These words will
help a reader/candidate identify the context of the passage. In return, it
helps find the correct answer.
§ Nouns and Verbs
§ Names (places, scientists, people and
more included in the passage)
§ Locations (towns, cities, states,
countries�)
§ Dates and Year ( 16th July 2008, 2011 AD)
§ Numbers or Figures ( 2 million , One thousand, 25%)
§ Capitalized or Italicized
words/phrases
§ Events and Occasions
What are
distractors in IELTS Reading?
To put it
simply a distractor is anything that looks like the correct answer but is
actually incorrect. They appear in different forms throughout the reading test.
The aim of this article is to teach you how to identify and avoid these
distractors/tricks.
Here are
some common forms of distractors that you can come across in the reading test:
Ø When you locate the correct section
in the reading text, there might appear to be two or three plausible correct
answers.
Ø Irrelevant options in a
multiple-choice question that also seem to be correct
Ø Phrases which include the keywords in
a question but do not lead to the correct answer
Ø Phrases in the passage that are only
partially correct or only partially match a question due to a difference in
qualifying words such as "some" or "few".
Questions for Reading Module in IELTS
General
information to learn about the types of questions in Reading Module:
1.
Matching
Headings (Lists of headings)
2.
Multiple
Choice Questions ( MCQs)
3.
Matching
Information
4.
Matching Sentence Endings ( Fill in the
gaps/blanks)
5.
TRUE/
FALSE/ NOR GIVEN
6.
YES/
NO / NOT GIVEN
7.
Short
answer questions ( word/s or a number)
8.
Sentence
Completion
9.
Note
Completion
10.Table Completion
11.Flow-Chat Completion
12.Diagram Labelling
13.Summary Completion With option
14.Summary Completion without option
Some
Questions in Reading Module may not follow order and these questions become
tough to find their answers as shown:
•
Matching
paragraph headings.
•
Which
paragraph contains the information?
•
Matching
names with statements or information.
For the
following question types, the answers are usually (almost always)
in order in the passage:
•
All
types of gap-fill (sentences, summaries, diagrams etc.)
•
True,
false, not given
•
Yes,
no, not given
•
Multiple
choice
•
Matching
sentence endings
•
Short
answer' questions
Some common tips for Reading Module
1) Be
patience, cool, and read the questions carefully with its instructions.
2) Don’t
expect to understand every words and their meanings.
3) Increase
your reading skills through different books, journals, magazines and newspapers.
4) Focus on
the instructions:
•
One
word and/ or a number
•
Two
words and/ or a number
•
Only
two words/ or a number
5) Don’t be
panic.
6) You
should paraphrase the words and its meaning in search of synonyms
7) Manage
your time. It is very crucial.
8) Ignore
anything you already know about the topic.
9) Practice
both slow and fast reading.
10) Be aware
while transferring your answers (especially in spelling, word, number)
11) Don’t
leave any questions blank.
1. Matching headings
This
question types requires you to match the headings in the question to correct
paragraphs or reading section in the text. There will always be more headings
that paragraphs or sections so that some headings will not be used.
Some useful tips to learn for it.
1 Pay
attention to the headings that are similar one another.
2 Find the
key words
3 Read the
paragraphs to get general idea
4 Especially
focus on the first and last sentences to get overview of the paragraphs.
5 The main
idea of the paragraph is your heading.
6 Read all
the headings before selecting correct heading as the answer.
Some useful strategies to learn
1 First read
each headings and then paragraphs
2 Circle/
underline keywords within the headings
3 Watch out
the similarities and differences among the headings
4 Skim to
find the general information of the paragraph
2. Multiple Choice Question (MCQs)
Multiple choice
questions appear regularly in both the Academic and General IELTS Reading
tests. They are fairly simple to complete but it’s easy to get tricked into
picking the wrong answer.
The aim of
this type of question is to test if you can:
•
Understand
the main idea of each paragraph
•
Scan
for specific information
•
Use
detailed reading to differentiate between several possible answers
There are
three different types of MCQ question. You will either have to:
1.
choose
one answer out of four options
2.
choose
two answers out of five options
3.
choose
three answers out of six options
The first
option is the most common.
You may
also have two different question forms. Either:
A.
completing
a sentence or
B.
answering
a question.
Some
useful tips to learn:
Read the
questions first. If you do this, you’ll know what you’re looking for when you read the
text which will save you loads of time.
The
answers will be in order. It’s very helpful to know that the answers come in order in
the text which isn’t the case with all question types. This makes it easier to
find them. So, if you’ve found answer 1 in paragraph 1 and answer 2 in
paragraph 3, you’ll know that answer 3 won’t be too much further on in the
text.
Read in
detail. For
some question types, you’ll be mostly skimming and scanning the text for the
answers. You’ll need these skills here too but with multiple choice questions,
the detail is important.
Watch out
for distractors. Be
aware that the test setters love to include ‘distractors’ in the answer options
to try and catch you out. A prime example is qualifying words such as every,
all, most, a few. They are only small words but they can completely change the
meaning of a sentence.
E.g. Everyone who ate the prawn sandwiches at the party was
ill.
Most people
who ate the prawn sandwiches at the party were ill.
Don’t
leave any blank answers. If you really can’t decide which answer is right, then guess.
There’s at least a chance that you’ll guess correctly and get the mark. If you
don’t put an answer, the question will be marked ‘wrong’ by the examiner.
Strategy
For Answering Multiple Choice Questions
1) Read
the questions
Carefully
read the questions. Don’t worry if there are words you don’t understand. If
they appear in the text, you may be able to work them out in context.
Alternatively, synonyms that you do understand may have been used.
2) Skim
read the text
On this
first reading of the text, you are aiming to get just the general meaning.
3)
Identify key words
Return to
the questions and underline key words in them. These will help you find the
location of the correct answer in the text.
4) Think
about meaning
Your other
task while looking at the answer options is to try and work out the difference
in meaning between them. Two may be very similar. Don’t spend too much time on
this but doing it will save you precious minutes in the next step.
5)
Predict the correct answer
From your
general understanding of the text, you may be able to make a reasonable
prediction of the right answer to some of the questions.
6) Read
the text again
Now re-read the text
a paragraph at a time, particularly scanning for the key words you identified
and likely synonyms. Remember that the answers will be in order so you can
expect the first one to be in paragraphs 1 or 2.
7)
Deciding between similar answers
It’s common to end
up with two very similar answer options that it’s difficult to decide between.
In this case, you need to study them in even more detail to identify the
difference.
Matching
Information
Matching
paragraph information questions are another type of question that comes up
regularly in the IELTS Reading test. Unless you have a good strategy for
tackling this kind of task, you can easily lose a lot of time on it.
Matching
information questions are a real test of your paraphrasing skills as the
information will be expressed in different ways in the statements and in the
text. Many synonyms will be used and sentence structures often altered.
The
statements could be reasons, descriptions, summaries, definitions, facts or
explanations. What they are doesn’t really matter. You are not expected to have
specialist knowledge in the reading test.
You do not
need to understand what the whole paragraph is about, just find specific
information in the paragraph and match it to one of the
statements. The answer will normally be contained in a whole phrase or
sentence, rather than a single word.
Important
tips and tricks to learn:
1) The answers will not come in
the same order in the text as the order of the list of statements.
2) Some paragraphs may not contain an
answer.
3) A paragraph could contain more
than one answer.
4) The answer will not
necessarily be in the main idea of a paragraph as in ‘matching headings’
questions. In ‘matching information’ questions, you will be looking for
specific information. Some students confuse these two types of question so be
sure that you know which you are answering.
5) Do the other questions on
this text first.
Each text
will have several types of questions attached to it. If you do the matching
information question last, you will have a good understanding of the passage by
the time you get to it. This will make it easier and quicker to complete.
6) Expect lots of synonyms.
Be particularly aware of information that can be represented in words and
figures. For example,
½ – a half
15º – fifteen degrees
69% – sixty-nine per cent
7) Usually, you’ll find the matching
information in a phrase or whole sentence, not in an individual word.
8) Search for the easiest
information to match first. This will usually be in a statement that contains
key words that are easy to find in the text such as names, numbers, places and
dates.
This way, if
time runs short and you’re forced to move on before completing the question,
you’ll at least have picked up the easiest marks rather than wasting lots of
time on a difficult question.
9) You can narrow down the match
of statement and paragraph by a process of elimination. For any specific
statement, there will be paragraphs that are clearly not a match.
The strategies to follow:
1 Carefully read the instructions.
2 Read the statements before you read the text. Take note of the
main idea of each statement and think about possible synonyms that might be
used in the passage.
3 Skim read the text to get a
general understanding of what it’s about.
It will help
you if you quickly identify the main idea of each paragraph and note it in a
couple of words beside the paragraph.
Although the
main ideas may not be the information you need to match, doing this will make
it quicker to find relevant paragraphs again.
4 Return to the statements. Read them
again and decide which one you think will be the easiest to match. Since the
answers won’t come in the same order as the order of the list of statements, it
doesn’t matter which you do first.
5 Once you’ve selected your
statement, scan the text for key words. When you think you’ve identified the
paragraph with matching information, read it in detail to check if you’re
right.
Expect
synonyms and paraphrasing to be used.
6 If you are right and can confirm the
match, fill in the answer sheet and cross through the statement to eliminate it
from further consideration.
If you’re
wrong, continue scanning for the correct paragraph.
7 Repeat this process until you have matched all the
statements to paragraphs.
Matching Sentence Endings
In IELTS
reading, might be asked to complete a ‘matching sentence endings’ question
type. In this question, you will be given a list of incomplete sentences with
no endings and another list with possible endings. Your job is to match the
incomplete sentences with the correct ending based on the reading text.
Tips for
Matching Sentence Endings
1.
The
answers are in the same order in the text as they are in the questions, so the
answer to question 2 will be after the answer to question 1 and so on. Locate
question one first and then you know where to begin.
2.
Try
to predict how each sentence will end before you look at the endings.
3.
Start
with the incomplete sentences first before you look at the endings or the text.
There are more endings than required, so looking at all of these in detail is a
waste of time.
4.
Think
of synonyms and paraphrases that the examiners could be using instead of
exactly the same words.
5.
All
of the sentence endings appear in the text, but you don’t need to read all of
them, just the ones that you decide to match with the incomplete sentences.
6.
When
highlighting keywords, it is often a good idea to highlight any names,
including place names, or dates. These are often easy to find in the reading
text.
7.
Don’t
just match words. Make sure the meaning in the reading text matches.
8.
Spend
more time on the first question because this is the most difficult. You have
lots of different options for the first question and it will take you more time
to work out the answer. The last question should take you much less time
because you have fewer options to choose from.
Some
strategies to learn
Some
strategies to learn
1.
Read
the question carefully.
2.
Read
the incomplete sentences first and don’t look at the endings yet. Try to
understand what they mean and highlight any keywords especially names, places
or dates.
3.
Predict
what the endings might be before looking at them. Think about what word type
(verbs, nouns, adjectives, adverbs) makes the sentence grammatically correct.
4.
Look
at the endings but not in too much detail. Try to see if there are any obvious
answers.
5.
Eliminate
endings that definitely cannot match. Think about grammar, collocations, and
meaning.
6.
Match
the endings you think might be correct. Write two or three options if
necessary.
7.
Find
the correct part of the reading text for each incomplete sentence. Be
careful with synonyms and paraphrases.
8.
Understand
the meaning of that part of the text and choose the correct answer.
TRUE, FALSE and NOT GIVEN
How to approach True, False and Not Given questions?
|
TRUE |
If the statement
matches the information in the passage |
|
FALSE |
If the statement
contradicts the information in the passage |
|
NOT GIVEN |
If the information is
not found in the passage |
Five
steps solving strategy for IELTS Reading True , False and Not Given.
Step1
Identify keywords in the statements.
Step 2
Identify similar words in the passage.
Step 3
Match the keywords in the similar words
Step 4
Evaluate if they are same, synonyms, opposites or if there is no match
Step 5
Decide whether the statement is True, False or Not Given
Important
Pattern to Notice in True, False, Not Given Questions
Consider the
statements and the corresponding equivalent statements from the reading
passage. Focus on:
Paraphrasing: Sometimes, there are chances of
getting rephrased sentences. It becomes easy to find whether the sentence is
True, False or Not Given.
Synonyms/Opposites: The best way to determine the
sentences is just by looking at the keywords which can be either synonym or
antonym.
Beware of
Some Common Mistakes
Beware of
Some Common Mistakes
Don't get
confused between False and Not Given.
This may sound obvious. But the statement does not necessarily have to be
either True or False. At times the information may not be given in the passage.
Never try to answer based on your prior knowledge of the topic.
The passage
could be slightly different from your prior knowledge of the topic. Making
assumptions can cost you a good IELTS score. Read the complete passage and then
answer the questions based only on the given information.
Quick
Tips for IELTS Reading True, False, Not Given
Ø The statements follow a chronological
order. Once you find the first answer, proceed to the next sentence.
Ø Watch out for those words that can
slightly change the meaning of the sentence. For example, many, some, never,
few, all, always, etc.
Ø Don't waste too much time on one question. If you can't find one, mark it Not Given.
Yes/No/Not Given Questions
This question is very similar to true/ false / not given. True/
false / not given always ask for whether or not certain statements agree with
the information given in the paragraph. Yes/No/ Not Given questions ask whether
or not certain statements agree with the writer’s views and opinions. If a
particular view is expressed in the passage, then we answer yes and
if not, then we answer no. Not Given refers to
information/ opinions that may have only been partially mentioned or not
mentioned at all.
The difference is in the type of information
contained in the text.
Yes/No/Not Given – the text will contain
the opinions, views or beliefs of the writer or other people
who are mentioned.
True/False/Not Given – the text will contain factual
information about a topic.
For Yes/No/Not Given questions, you will be
given a set of statements and a text. Your task is to decide which of the
following applies to the information in each statement:
·
it agrees with the views
of the writer – YES (Y)
·
it disagrees with or
contradicts what the writer thinks – NO (N)
·
it is impossible to know
what the writer’s point of view is – NOT GIVEN (NG)
Some useful tips and techniques to learn
1) The answers appear in the same order in
the text as the order of the statements.
2) You don’t need to read the whole text.
First, you will scan for keywords and then you’ll read in detail the section in
which they're located to find the answer.
3) There will be at least one of each answer
type – Yes, No, Not Given. So, if you don’t have at least one of each when
you’ve completed the question, you’ve made a mistake.
4) Watch out for distracters. Be aware
that the test setters love to use ‘distracters’ to really test you. A prime
example is qualifying words such as:
every
a
few
all
always
some
often
most
occasionally
These single words can
completely change the meaning of a sentence.
E.g. Julio often goes to the gym after work.
Julio occasionally goes to the gym after
work.
In Y/N/NG questions, the
meaning of the statement must be an exact match with the
opinion of the writer for the answer to be YES.
5) Also be on the lookout for qualifying
words that express possibility or doubt such as:
seem
claim
suggest
possibly
believe
probably
Again, they can totally
alter the meaning of a statement.
E.g.
He claimed that profits had gone up by 10%.
He knew that profits had gone up by 10%.
6) The view or opinion of the writer may not
be immediately clear from the text. You may have to determine this through what
they say.
7) The statements will contain synonyms and
paraphrasing so be on the lookout for these.
8) Remember that at least one answer will be
NG. This means that you will be searching for information that is not there.
Short answer question
Short-answer
questions on
IELTS Reading are very similar to sentence completion questions. Again, you
should answer questions with words taken directly from the text. And you’re given
a word limit (for example: write no more than two words). Similarly, short
answer questions are the open-ended questions that need you to write an answer.
Commonly, they are used to evaluate the basic knowledge and understanding.
Furthermore, Skills like ability to skim the paragraphs and understanding the
meaning, proficiency in scanning the certain information, understanding the
question, identifying keywords and thinking of possible paraphrases and
synonyms of keywords are judged.
1.
Read
the instructions carefully - these tell you how many words you can use (a
maximum of three in this case).
2.
In
IELTS short answer questions you should use words from the text rather than
your own, and don't change the words.
3.
Quickly
read through all of the questions so you can get an idea of what information
you will have to find in the text.
4.
Use
key words from the question to help you skim the text quickly to find the
information. For example, in the first one, you need to look for "type of
care".
5.
Remember
though that synonyms will also be used in the text, so you must be careful when
you look for the information.
6.
Read
the section of the text where you know the answer is carefully to see which
words will answer the question.
7.
Your
answer must make sense grammatically to be correct.
Answering
strategy:
1.
Skim
over the text.
2.
Read
the question and find the paragraph, which is likely to contain the answer. Use
key words to navigate.
3.
Read
attentively the paragraph you’ve found, searching for the answer.
4.
Once
you've found the answer, check if it doesn't exceed the word limit.
5.
Repeat
this strategy with other questions.
Sentence Completion
Sentence
completion questions are common in the IELTS Reading test. As long as you have
a good strategy to answer them and have done lots of practice before the exam,
they shouldn’t give you too much of a problem.
You will
be given a set of four or five sentences with gaps in them.
You are
required to fill the gaps with appropriate words to complete the meaning of the
sentence.
The
instructions will tell you how many words you are allowed to use to fill the gap.
Read them very carefully. They will most likely tell you to use ONE
WORD ONLY or NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS.
If you use
the wrong number of words, your answer will be marked incorrect even if the
information you give is correct.
The
instructions will also state whether you have to use words taken from the
reading text or if you can use different ones, that is, synonyms.
Skills
you need
This type of
question tests your ability to:
Identify
synonyms
Understand
paraphrasing
Scan for
specific information
Read in
detail for meaning
You need a good knowledge and understanding of synonyms and paraphrasing for
all IELTS Reading questions but they are particularly important in sentence
completion questions. Here’s a quick reminder of what each of them is.
Synonyms are words that mean exactly or
nearly the same as a given word. For example, for the word ‘true’ you could
also use, ‘genuine’, ‘accurate’, ‘factual’ or ‘correct’.
Paraphrasing is saying the same thing in
different ways, using different words and/or a different sentence structure.
For example,
a) The new restaurant was small and cosy and the food
excellent.
b) The cuisine served in the new eatery was
superb and the atmosphere intimate.
These
synonyms have been use:
restaurant à eatery
small and
cosy à intimate
food à cuisine
excellent à superb
Some
important tips and tricks to learn
1) Read the instructions
carefully to find out:
a) how many words you should write for the
answer.
b) if you have to use the exact words from the
text or can use synonyms.
2) Read the sentences before you read
the text. It’s a waste of time reading the passage first as you don’t know what
information you’re looking for until you’ve read and understood the sentences.
3) The answers appear in the
same order in the text as the order of the list of incomplete sentences.
4) The completed sentences must be
grammatically correct. If they aren’t, then you have the wrong answer.
5) When first studying the sentences,
try to work out what type of word is missing, e.g. a noun, a verb, an adjective
or an adverb. This will help you to find it more quickly.
6) Scan to find the location of the
answer, then read in detail to find the answer itself.
7) Always be thinking about synonyms and
paraphrasing. Look for matching meaning rather than exact word matches when
comparing the information in the sentences and the text.
Table/flow chart
The
information in the table or flowchart will match information in the text but it
will very likely be paraphrased and include synonyms.
Once you’ve
located where in the text the answer is located, you'll need to interpret the
language to identify the word or words you need to fill the gap in the table or
flowchart.
This type of
question tests your ability to:
1.
Scan
for specific information
2.
Skim
for general meaning
3.
Understand
paraphrasing
4.
Identify
synonyms
5.
Read
in detail for meaning
Some
useful tips and tricks to learn
a)
Table
completion and flowchart questions are not as hard as they look. If you apply
the step-by-step strategy I explain below, you shouldn’t have too many problems
answering them.
b)
This
type of question can be presented in several different forms, especially in the
case of flowcharts, so may not look exactly like either of the examples I’ve
given you.
c)
Don’t
panic if the layout is unfamiliar. What you need to do to complete the task
will be the same however it might look.
d)
The
information in the table may appear in a different order to the matching
information in the reading text.
e)
Fill
the gap with the exact words from the text. Don’t use synonyms or your answer
will be marked incorrect.
f)
When
first studying the table, try to work out what type of word is missing, e.g. a
noun, a verb, an adjective or an adverb. This will help you to find it more
quickly.
g)
Always
be thinking about synonyms and paraphrasing. Look for matching meaning rather
than exact word matches when comparing the information in the table and the
text.
h)
Scan
to find the location of the answer, then read in detail to find the answer
itself.
i)
The
completed sentences must be grammatically correct. If they aren’t, then you
have the wrong answer.
j)
Use
any little clues that are present in the table to help you understand the type
of information you need to find. For example
k)
You
don’t need to understand everything. Even if some of the vocabulary is
unfamiliar, you'll probably be able to work out the answer from context and
other clues.
Diagram Labelling
In IELTS academic reading a diagram will be
given, for which you have to label the parts referring to the passage. You may
find it challenging to solve diagram labelling questions but our tips will
guide you to tackle this question.
In this task a diagram explaining a scientific or natural
process or structure of a living or non-living thing is presented. Your task is
to fill specific parts of the diagram with text or word from the reading
passage.
There’s no need to worry as you don’t need to fully
understand it. Simply use the information given, just as you do with every
other type of question.
You will find the followings.
§ You will be given a diagram or a
plan.
§ You are required to label specific
parts with words from the text or a word list.
The diagram will be one of the following:
§ A design or plan
§ A technical drawing, e.g. a machine
or invention
§ A diagram of something in the natural
world
If you are
required to select words from the text for the answers, you'll be told how many
words you’re allowed to use for each label. For example, ONE WORD or NO
MORE THAN TWO WORDS. Hyphenated words such as ‘mother-in-law’ count as one
word.
If you use the wrong number of words, your answer will be marked incorrect even
if the information you give is correct.
Some
useful tips and techniques:
1) Diagram labelling questions
are not as hard as they may at first seem. If you apply the step-by-step
strategy I explain below, you should be able to master them.
2) Don’t panic if the diagram looks
complicated. It won’t be. A diagram is just another way of presenting
information – a combination of language and a drawing.
You need no
prior knowledge of the subject in order to complete it. Remember, this is a
test of your reading skills, nothing else. Again, just follow the strategy.
3) Use any little clues that are
present in the diagram to help you understand it. In our diagram, for example,
we have,
Some
numbers
Some text
One
completed label
A heading
in the word list box
Each gives
you important information about the topic and will be related to the answers in
some way. I’ll show you how to interpret it below.
4) You may be given a glossary of
key words that could be unfamiliar to you. They’ll be below the text. Here’s
the glossary for this question.
Glossary
1. dung:
the droppings or excreta of animals
2. cowpats: droppings of cows
5) Try to get a general
understanding of the diagram before you read the text.
6) Scan for keywords in the text
to locate the paragraph with the answer in then read in detail to identify the
words or words needed for the label.
7) The information in the text
that contains the answers will very likely include synonyms so be on the
lookout for them.
8) If you're struggling with a
particular label, move on. Grab the easiest marks and come back to relook at
the others later if there's time left at the end.
Make an
educated guess if you have to rather than leaving the answer blank. You may
guess correctly and score the point.
Summary completion questions appear regularly in the IELTS
Reading test so you need to learn how to answer them.
First, I would like to
make you understand what a summary is.
A summary is: ‘a
short, clear description that gives the main facts or ideas about something’.
In this case, it’s a short summary of information from part of the text that’s been set for your reading test.
For summary completion
questions, you will be given:
1) The
text.
2) A
summary of information from a section of the text with some gaps where words
have been missed out.
Summary Completion is mainly found in two types as shown below.
A.
Summary Completion (with option)
B.
Summary Completion (without option)
Summary Completion
Summary completion questions appear regularly in the IELTS
Reading test so you need to learn how to answer them.
First, I would like to
make you understand what a summary is.
A summary is: ‘a
short, clear description that gives the main facts or ideas about something’.
In this case, it’s a
short summary of information from part of the text that’s been set for your
reading test.
For summary completion
questions, you will be given:
1) The
text.
2) A
summary of information from a section of the text with some gaps where words
have been missed out.
Summary Completion is mainly found in two types as shown below.
A.
Summary Completion (with option)
B.
Summary Completion (without option)
Selecting from a list of words or phrases
* Note that there are more words in the list than are needed to
fill the gaps.
Selecting words from the text
Skills
needed
This type of question tests your ability to:
1.
Skim the summary for general meaning.
2.
Scan the text for specific information.
3.
Identify key words.
4.
Recognise synonyms & paraphrasing.
5. Use context to make predictions.
The Strategies to use
1. Carefully read the
instructions taking particular note of where you should get the missing words
from – a word list or the text. If it’s the text, note the word limit for your
answer, e.g. no more than two.
2. Skim read the summary to
get a general understanding of what it’s about.
3. Next, read the summary in
more detail and try to predict the type of word needed to fill each gap, e.g.
verb, noun, adjective, and what that word might be. Don’t spend too long on
this but it will save you time later if you do it.
4. If the question includes a
list of words, see if you can guess any answers. You may be able to narrow it
down to 2 or 3. There will be others that will obviously be wrong.
5. The summary will normally
relate to one section of the text, probably 2-3 paragraphs. Your next job is to
identify this.
6. Pick out a few key words
from the summary to scan for. Names, numbers, places or dates are ideal if
there are any in the summary as these will be easy to spot. Remember that
synonyms could be used. When you’ve made your selection, scan the text for
them.
7. Read the first sentence of
the summary with a gap in it. Try to work out what form of word will fit, e.g.
an adjective, the past tense of a verb, a countable noun. You may even be able
to predict the missing word itself or a synonym.
8. Identify one or two key
words and scan the section of text for them, watching out for synonyms and
paraphrasing.
9. When you’ve found the part
of the text with the answer in, read it in detail to identify the word you
need, either in the text itself or from the word list.
10. Check your answer to
ensure that the sentence is grammatically correct.
11. Repeat this process for
the rest of the missing words.





No comments:
Post a Comment